Critical thinking is a vital skill in today's complex world. Here are seven key elements to cultivate and enhance your critical thinking abilities:
1. Questioning: Begin by questioning assumptions, biases, and information presented. Ask "why" and "how" to delve deeper into the root of issues and understand different perspectives.
2. Analysis: Break down complex ideas or situations into smaller components to examine them systematically.
3. Interpretation: Develop the ability to interpret and evaluate information objectively. Consider the credibility of sources, context, and possible interpretations.
4. Inference: Draw logical conclusions based on evidence and reasoning. Identify the implications and consequences of different scenarios.
5. Evaluation: Assess the validity, relevance, and reliability of information and arguments.
6. Explanation: Articulate your thought process and reasoning clearly. Communicate ideas effectively, providing evidence and logical support.
7. Self-Regulation: Reflect on your own thinking processes and biases. Be open to new information and perspectives.

What are some of the best examples of Creative Thinking?
To understand creative thinking better, here are a few examples that will give you interesting ideas.
Example 1 Situation:
What is the social structure of the Mayan Civilization?
Creative Ideas:
- You can create or express how the Mayans were the first to bring brew beverages out of cocoa.
- You can do role-play enacting Mayan Civilization
- You can make a model of the Mayan calendar
- Use Mayan words to write assignments
- You can use Mayan Numerical System etc.
Example 2: Situation:
Write an assignment about Recent Space Inventions?
Creative Ideas:
- Include images of recent science trends and innovations
- Include top science minds speeches related to your assignments.
- You can make bookmarks/page separators as a ‘print and cut version of science people or science-project figures’.
- You can do presentations with more graphic elements and live clips of launching that space invention.
- Use reverse-thinking to write assignments differently than the usual format. But make it meaningful.
- Add artworks in your assignments
Example 3: Situation:
Creativity in the workplace
Creative ideas:
- Maintain a positive workspace.
- Add positive elements to your desk
- Note down meeting points diagrammatically
- Do artworks or drawings to represent your tasks to do.
- You can keep motivation flyers stuck in a pinboard.
Example 4: Situation:
To showcase your skills and talents
Creative ideas:
- Build a nice Portfolio
- Prepare a creative, crisp and minimalistic resume
- Develop a blog to showcase your work
- You can include testimonials of people whom you have worked
- You can develop a viewbook
Example 5 Situation:
How to analyze this problem?
Creative ideas:
- Draw doodles to represent problem factors
- Develop a mapping system to connect with the problems
- Use flowcharts, diagrams, analogies, etc. to represent a problem.
Today’s professional world is looking for people who are both critical thinkers and problem solvers. On the surface, they can look similar. But, critical thinking and problem-solving have their fair share of differences and thought processes.
The 5 Common Steps in Critical-Thinking and Problem-Solving are:
1. Identify the problem:
The first step in critical thinking and problem-solving is problem identification. For a critical thinker, the thought process will be:
- Is it a real problem
- Does the problem exists
With a problem-solving attitude, the thought process will be:
- This is a problem
- Here to start to analyze it
2. Analyze:
You analyze and interpret the problem.
3. Brainstorm:
Similar to evaluating step in critical thinking, this brainstorming session is about:
- Finding solutions
- Analyzing the pros and cons of the solution
- Justifying the solution
4. Decide:
You come up with an agreeable solution here.
5. Take action:
You take actionable steps to put the solution into action.
...............................................................................................................
To make things understandable further, here are
6 Main Difference between critical thinking and problem solving
Difference #1
Critical thinking is: Intentional, reflective way of looking at surroundings, things, or scenarios.
Problem-solving: Focuses on a specific situation
Difference #2
Critical thinking: It involves finding a workable solution and defending/justifying the solution.
Problem-solving: Forming a conclusion.
Difference #3
Critical thinking: Recognizing the problem scenarios
Problem-solving: Defining the problems
Difference #4
Critical thinking; Identifying, formulating and solving problems
Problem-solving: Recognizing a problem situation
Difference #5
Critical thinking: Encloses all thinking skills, decision-making abilities, and problem-solving factors.
Problem-solving: It is an outcome of critical thinking
Difference #6
Critical Thinking involves steps like: Analyzing, Reasoning, Evaluating, Synthesizing, and Take Action
Problem Solving involves steps like: Identifying the problem cause, brainstorming sessions, come up with multiple solutions. And, monitor the progress.
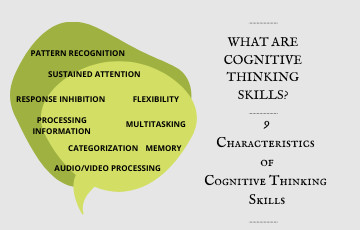
What are Cognitive Thinking Skills?
Cognitive thinking skills are like the heart of all thinking skills. You read, learn, process, see, pay attention, remember, process new information, grasp, keep data, and process everything by cognitive thinking. Only with cognitive thinking skills, we see, understand, and look at the world as it is.
9 Characteristics of Cognitive Thinking Skills
Sustained Attention:
It is the ability to pay sustained attention over for a consistent period.
The longer you can pay attention, the better you become in understanding and keeping it in memory.
Response Inhibition:
It is your ability to stay focused and remain attentive despite what’s happening outside.
If you don’t respond to distractions often, it means, you have better ‘response inhibition’.
Information Processing Speed:
It is your ability to process additional information, existing information or incoming information quickly.
Cognitive Flexibility:
When you are in a place, you change your mind and become flexible about it.
For instance, you behave a certain way at interviews. You behave a certain way with friends. you switch mentally between these two scenarios. This is called cognitive flexibility.
Multiple Attention:
It involves successful multitasking. It requires speedy processing of information, attention, and good planning.
It is not possible all the time for everyone.
Working Memory:
You remember the instructions, procedures and the entire process long enough in your memory.
It should come to you even after a long time to perform the process correctly.
Category Formation:
It comes under the higher order thinking levels.
Category formation says your ability to process information and categorize them accordingly.
Pattern Recognition:
It is your ability to understand pattern, logics and meaning behind things you see, things you hear and with the work you do.
Audio/Visual Processing:
It is your ability to grasp and interpret the audio, video elements around you.


Logical Thinking Skill:
Logical thinking looks for things that make “sense”. Logical thinking skills are reflected in the way you:
- Question
- Reason
- Think
- Form opinions
You classify what is appropriate and judge what is right based on a given set of logic.
Characteristics of Logical Thinking Skill:
- Logical thinking skills are more of a sequential thought process.
- People are not born with logical thinking skills. People practice it and perfect it.
- Logical thinking skills pay close attention to details.
- Logical thinking skill considers facts, details, data, patterns, and perceptions.
- There is no place for emotional aspects or biases in logical thinking.
- An Important characteristic of logical thinking is, you will reject thoughts like “I don’t know” or “it is too difficult” or “I can’t do this”.
- If trained in logical thinking, people get smarter and sharper. Logical thinking can be perfected by constant practice.
- Logical Thinking helps you take better decisions, give productive results, and reduce complexities.
- Logical thinkers are good solution-givers.
- Logical thinking skills can be enhanced by playing puzzles, mental challenges, solving crosswords, math games, word games, etc.
You can understand what logical thinking is through different examples here.
Ex 1: What if someone says This Street brings Poor luck?
Logical Thinking would be:
· It is a much-generalized point.
· Does this street bring bad luck to you or everyone? If so, where is the proof?
· Has everyone gone through this street experienced bad luck?
· How many people can verify it?
Ex 2: I am living in Stockholm. I am living in a Nordic Country.
Logical Inference:
Facts are verifiable because Stockholm is in Sweden. The countries Sweden, Denmark, Finland, and Norway are all referred to as Nordic Countries.

1. Remembering Skills:
Remembering skill is the brain’s ability to remember, identify, and interpret what it sees and what it hears.
Recalling, memorizing, retrieving and repeating information from your brain whenever needed is a unique aspect of this thinking skill.
Associating Words: Bookmark, Count, Describe, Enumerate, Identify, Label, List, Match, Recall, Sequence, Tell, Remind, Recite, Find out.
2. Interpreting Skills:
The second stage of thinking is interpreting. Your mind becomes curious and asks questions like “what is it”, “why is it like that”, “who put it here”, “where it came from” etc.
Associated Words: Conclude, Discuss, Describe, Explain, Illustrate, Predict, Reports, Tell, Express.
3. Application/Implementing Skills:
Implementing skill is about “what you have to do” and “what has to be done”. By the knowledge and resources you have, you solve a problem.
Associated Words: Implement, Imitate, Show, Reveal, Produce, Choose, Gather, Use.
4. Analyzing/Scrutinizing Skills:
Systematically and logically you break the problem elements at this level. You disengage irrelevancies. You differentiate, compare, examine, categorize and experiment your problem-scenarios.
Associated Words: Characterize, Categorize, Classify, Compare, Predict, Rank, Redefining, Outlining, Subdivide, Research, Represent, Map, Diagrammatic Representation.
5. Judgmental Skills:
You draw conclusions based on facts and data. You justify your standpoint in this stage. To justify, you assess, support, evaluate, find credibility to your solutions and communicate it to people. Evaluation and judging is a crucial thinking skill.
Associated Words: Test, Compare, Critique, Defend, Rank, Judge, Justify, Argue.
6. Creative Skills:
Creativity is a higher-order thinking skills different from others. We can combine it with other thinking skills. Or, we can use it independently.
Associated Words: Invent, Modify, Reverse-Engineer, Rearrange, Networking, Revise, Remodel, Out of the Box, New Framework.
Conclusion:
The above are 6 major categories of thinking skills we see. And are based on bloom’s taxonomy of critical thinking.

Explore the 9 major types of thinking skills essential for problem-solving and decision-making. Enhance your cognitive abilities for success.
1. Analytical Thinking:
Analytical thinking skill is your ability to analyze a given the problem, or situation step by step. You perform a complete analysis of all possible ways to interpret the situation/problem before you.
2. Divergent Thinking:
In short, divergent thinking skill is “Go diverse. Conclude with one that works”. Divergent thinking involves exploring all possibilities and viewpoints to find an appropriate solution.
First, you begin gathering related facts, data, or references from all sources. You analyze and apply logic to find the relevant possibilities. Among them, you pick the one that stands out and seems to be precise to solve the problem.
3. Convergent Thinking :
Convergent thinking is about connecting all the dots. You connect scattered thoughts, data, standpoints, or related information and put together one big picture. Convergent thinking is a key thinking skill we need in life.
4. Critical Thinking:
It covers 7 steps like identifying, gathering, analyzing, interpreting, establishing, deciding and communicating the problem.
5. Creative Thinking:
Imagination and creativity proceed here instead of logic and reasoning.
6. Abstract Thinking:
Abstract thinking is like abstract art/painting. Change your normal perspective to see what is being portrayed. Find the hidden meaning. You see the 'actual' truth behind the 'false' truth.
7. Concrete thinking:
As the name suggests, concrete thinking is factual thinking. Only facts and nothing else. A concrete thinker will approach everything with facts, data, and solid knowledge. It is the opposite of abstract thinking.
8. Sequential Thinking:
You think and process in an orderly, sequential manner. You don’t deviate. You progress step-by-step i.e. you can go to the second step only after your first step is complete. Every step in interconnected sequentially here.
9. Holistic Thinking
You go straight for the big picture and then you connect everything.
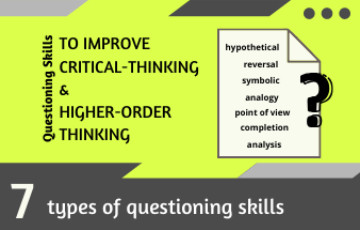
Hypothetical Questions:
Hypothetical questions kindle your brain to look for possibilities and fresh ideas. Hypothetical thinking enables an individual to anticipate, predict, and describe the pros and cons.
Examples:
- What will happen if I remove this?
- What will you do if this happens?
Hypotheses are good for exploring prospects. It also helps you in preparing a contingency approach.
Reversal Questions:
Reversal thinking makes an individual 'twist the problem in reverse or sideways' to understand it. It brings out alternate possibilities to deal with problems.
Examples:
- In what ways we are complicating this problem?
- Why should we not include it?
- What happens when we don’t resolve it?
Symbolic Questions:
This type is about using multiple formats to understand a solution.
Example:
We can use a chemical equation structure to explain what is happening inside a tree.
Analogy Questions:
It’s the most common type of questioning. We compare and correlate here.
Example:
- What is the physics behind birds flying?
- What is the connection between a chemical-reaction and cooking?
Point of View Questions:
Here, you put yourself in a different shoe and ask questions and answer them. This questioning skill is important in improving critical and higher-order thinking.
Example:
- How will my boss think?
- How will an experienced person handle this?
Completion Questions:
It is like “fill in the blanks”. The questions will end abruptly. We have to use our imagination to close it appropriately.
Example:
- What happens after this stage?
- How did it disappear?
Analysis Questions:
It is like a spider spinning a web. You ask a web of questions instead of raising basic questions. You go deeper levels and look for patterns and ideas.
Example:
- What are the effects? Where it is extending?
- What happens there if I do this here?


Learn how to craft effective higher-order thinking questions to stimulate critical thinking and deepen understanding. Enhance learning outcomes and engagement.
Science and Psychology suggest that asking Higher Order Question promotes critical thinking levels in individuals.
What are Higher Order Questions (HOQ)?
High Order Questions are entirely different from normal questions. With normal questions, you recall and remember what you know, and answer. With HOQ, you apply, analyze, synthesize, and evaluate information and conclude with a solid answer.
Based on three levels of Higher Order Thinking, here are some of the best higher-order questions that you can refer to or use to improve your critical thinking abilities.
Level 1: Analysis - Higher-Order Questions
- How does it (Problem/solution/inferences/idea) work?
- What causes it?
- Is there another cause?
- In what way it happened?
- What technique we can use?
- Is the data relevant?
- What kind of problem is this?
- What is the correlation between this problem and the present situation?
- Is there any pattern?
- What is irrelevant to this problem?
- What are the pros and cons?
Level 2: Synthesize - Higher Order Questions
- What is the value?
- How can you verify it?
- How do you support this response?
- What is the majority suggestion?
- What will you suggest?
- What choices We can make?
- How to prioritize the data?
Level 3: Evaluation - Higher Order Questions
- How to generate a plan?
- What happens if?
- What facts are verified? And, what facts are irrelevant?
- Where could you bring innovation?
- What are the alternatives?
- Is the answer convincing?
- Is it a well laid out plan?
- What to do when the solution fails?
- Why this method is suggested?
Takeaway:
By answering these HOQ, you improve your cognitive, logical, critical and strategic skills.

Lower Order Thinking Skills are basic qualities we need to develop to become good at critical thinking. Lower-order thinking improves problem-solving and decision-making abilities in us.
6 Techniques to Improve your Lower Order Thinking Skills:
1. Be Willing to Hear:
Lower Order Thinking skills are about grasping the basics. You can grasp the basics of anything by
- Listen to what other people have to say.
- Refer to multiple resources.
- Gather opinions.
- Cross-check and validate facts.
- Look for real-time experiences.
Develop your mind to grasp the basic things around you easily. Avoiding complications is one way of improving LOTS.
2. Be aware of what’s going on:
How will you understand the problem if you don’t know what is going on? So, be aware of what’s happening around you. Mindfulness is a basic quality you need for boosting Lower Order Thinking.
3. Describe the problem in your way:
By understanding problems your way, you become closer to interpreting it and finding a solution. Ask Questions to understand the problem even closer.
You can write, doodle, mind-map the problems in your way. It improves your understanding and logical thinking.
4. Make Inferences:
Write what comes to your mind about the problem. Refer to previous sources related to the problem. Do groundwork. Gather necessary data.
Come up with clear and crisp inferences of:
- What is this concept?
- What does it say?
- Where can it be applied?
- Why it is applied? Etc.
Getting logical inferences is a simple way to boost your Lower Order Thinking.
5. Improve Memory:
Remembering and recalling is key to Lower Order Thinking. To improve your memory power. Play brain games and memory exercises in your free time.
6. Bring Interest:
Interest and self-motivation are important to boost thinking skills in individuals. Without self-interest, even a critical thinking mind becomes lethargic.

Gain insights into lower-order thinking skills and their significance in learning and problem-solving processes. Expand your understanding.
Lower-order thinking skills (LOTS) form the building blocks necessary for advancing to higher-order thinking skills (HOTS).
Lower-order thinking skills encompass fundamental abilities individuals acquire during their developmental stages, including:
Observation
Memorization
Recollection
Comprehension
These skills are cultivated throughout the foundational stages of education.
A scientifically proven fact is “The more skillful you are at Lower Order thinking, the more capable you become at Higher Order Thinking”.
3 Levels of Lower-Order Thinking Skills
According to Bloom’s taxonomy of critical thinking, there are three levels within the Lower Order Thinking Skills category:
Recollection
Comprehension
Application
Level 1: Remembering - Assessing Your Ability to Recall Information
At this initial level, one's proficiency in:
Defining
Recalling
Recognizing
Comprehending
Identifying
And adopting selective approaches, are fundamental skills within the domain.
Moreover, it involves:
The capacity to identify problems.
Recalling past experiences to detect patterns or similarities.
Level 2: Understanding - Gauging Your Capacity to Explain Previous Perceptions
The understanding phase hinges on your capability to:
Explain
Describe
Paraphrase
Infer
Summarize
Classify
Compare data gathered from the preceding level.
Understanding is pivotal within Lower Order Thinking as it encapsulates a succinct grasp of the underlying problem.
Level 3: Applying – Implementing Inferences Drawn from Levels 1 and 2
This stage revolves around:
Solving
Operating
Executing
Choosing
Demonstrating ideas gleaned from earlier levels.
It entails devising concrete strategies to progress towards higher levels of critical thinking.
Key Insight:
Just as climbing a mountain begins at its foothills, developing strong critical thinking skills entails honing Lower Order Thinking Skills before advancing to Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS).

1. Redefining:
People with higher-order, thinking skills can redefine the entire problem in a completely fresh angle. We wouldn’t have seen it before.
2. Flexibility:
Flexibility is:
- Adapting to new situations
- Improvisations
- Shifting strategies
- Welcoming fresh perspectives to meet any challenges.
When you adopt higher-order thinking, you improve your flexibility levels. The more flexible you become, the more thoughts and viewpoints you perceive. In turn, it improves your critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
3. Ability to create original Ideas:
When you adopt higher-order thinking, it improves your originality. It kindles your creativity.
Want to know how?
Higher-order thinking abilities will stimulate the brain to look for wider possibilities to resolve the problems.
You observe, question, listen, analyze, process, and validate everything around you. This critical thinking stimulates you to find what is needed. And, see what new changes can be made.
You will think about new frameworks/strategies to use. You become curious. It all leads to drawing original ideas.
4. Always Looking Forward:
Critical minds are curious minds.
That too, people who adopt higher-order thinking in their approaches are
- Always curious, analytical, and logical.
- They look forward to anything and everything in their life.
- They are never afraid of changes and challenges.
- They keep looking forward to facing new things and meet new people.
- They gain more knowledge.
- They widen their mental abilities.
If you want to be a better critical thinker and bring high order thinking skills, keep looking forward and challenge yourself.
5. Tolerating Ambiguities:
The key quality of higher-order thinking skills is, people will tolerate uncertainties, and ambiguities irrespective of any situation in life. It makes them highly resilient than the rest.


Higher-order thinking abilities will carry your critical-thinking levels to a peak. Here are lists of 5 higher-order thinking skills you should follow in your life. It not only improves your critical thinking abilities but also makes you highly productive.
1. Being Original:
By being yourself, you realize your strengths, weaknesses, abilities, and improvement areas. Once you know yourself, you align your thinking accordingly. By being an authentic person, you enhance your originality and creativity in things you do.
2. Using Imagination:
Critical thinking starts with imagination. If you can imagine different outcomes, perspectives, and possibilities for a problem, it means your higher-order thinking abilities are growing.
3. Finding Purposes:
Higher-order critical thinking has made many people find their true purpose and passion. When you start thinking critically in life, you will identify
- What do you want?
- What works?
- What doesn’t fit?
- What is irrelevant?
- What are the future possibilities?
- Will this education/career work for me? Etc.
These questions form the basis of finding your purpose in life. Among the list of higher-order thinking skills, ‘Finding Purpose’ is the most interesting and stands out.
4. Ability to Accept Changes:
Brian is a mix of ‘constant changes’ and ‘existing systems’. Accept new changes. Your brain will combine and connect new changes with existing data. Your critical thinking improves. The result is, you become efficient in finding better perspectives.
5. Open-Minded Thinking:
Your higher-order thinking levels improve when you become open-minded and accept things. Higher-order doesn’t work when your mind is narrow and doesn't see the world positively.
Takeaway:
The above list of higher-order thinking skills determines an individual’s critical thinking levels and helps them improve better.

1. Practice Problem-Based Learning:
Problem-based analysis and learning are vital to separate relevant and irrelevant variables from the problem equation.
- Get valid data to process.
- Study the previous groundwork.
- Consult with people who have handled similar challenges.
- Refer related-documents and data, etc.
Example: If you are a student, you can engage your higher-order thinking skills by using project-based learning. You can learn via relevant websites, podcasts, documentaries, expert opinions to gain more knowledge than textbooks.
2. Do Authentic Assessment:
How you process your data is important to improve your high order thinking. You have to be authentic in your assessments to bring out facts and truth. Despite different methods and resources, assessing problems based on real-world the approach brings more authenticity.
3. Inquiry:
Inquiry is about
- Identifying relevant and necessary questions
- Self-validating the questions.
- To check the importance of problem questions with real-world scenarios
- Planning answers
- Testing the answers
The quality of questions determines the quality of thinking. So, excellent questioning skill improves and engages higher-order thinking ability in you.
Example: You can do brainstorming or do forum-type discussions, etc.
4. Practicality:
Approaching circumstances logically, practically, and reasonably is necessary. Be practical in approaching a problem instead of letting emotions in. Become more self-aware of the work you do.
5. Get Feedback:
You won’t know how you are doing until someone points the right and wrong.
6. Pick Appropriate Tools:
Use technology. Pick tools and methods that are comfortable for you. And it should align with your way of working. Appropriate tools to break down problems are important in high order thinking.
7. Implementing “20 Time”:
Spend 20% of your time every day to work on things that benefit and improve yourself. This is a strategy used by Google for its employees.

1. Improve your Metacognition:
Metacognition refers to realizing oneself. Metacognition is about what you know, what you don’t know, your ability to understand, control, and process your cognitive process.
Metacognition is short is:
- Knowing your strengths and weaknesses.
- How to compensate for your weaknesses?
- How to take advantage of your strength?
- Looking for a creative place to showcase skills, etc.
Metacognition is key for developing Higher Order Thinking.
2. Approach/Type
Make sure that any problem/concept is approachable verbally, non-verbally, concretely, or abstract. Based on the nature of the problem, you must categorize it as a verbal/non-verbal type or concrete/abstract type.
3. Concrete to Abstract and Vice versa:
To understand the problem better, you either move from a tangible, concrete approach to a non-tangible abstract approach. For instance, if the problem is an abstract type, you can use concrete, real approaches to visualize and analyze the problem.
4. Question and Answer:
Ask questions based on
- Textual/base information
- Recent inferences,
- Prior knowledge
You can have a closer look at the problem.
5. Identifying the Problem:
Identify “it’s a problem” the moment you see it. Avoid making late inferences. Be quick. This skill is primary for boosting higher-order thinking abilities.
6. Collaborative ‘Thinking’ Strategies:
As the name shows, the collaborative strategy is, including analytical, practical, and creative thinking skills to approach a problem.
The analytical approach is about: Comparing, Contrasting, Evaluating, Analyzing, and Self-critiquing.
The Practical Approach is about: how to use strategies, how it applies in the actual world, how to use resources effectively, how to implement solutions, etc.
The Creative Approach is about: Inventing novel ideas, imagining, and designing.
Among the six strategies to develop higher-order thinking, we consider Collaborative strategy to be the most resourceful.

Explore the 3 levels of higher-order thinking and enhance your cognitive abilities. Develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity skills.
1. Analyzing:
“Analysis is the critical starting point of strategic thinking.” – Kenichi Ohmae
The first level of Higher Order thinking is, doing a thorough analysis. You get to analyze the entire problem here.
You do activities like:
- comparing the problem with previous groundworks
- look for any similarities
- compare background knowledge
- Have brainstorming sessions
- Break the problem to understand better
- Hear multiple opinions.
- Organize your findings to get a detailed study of the problem.
2. Evaluating:
“It is only through evaluation that Value Exists.” – Friedrich Nietzsche
Evaluation is the key.
In this ‘Evaluating’ level of higher-order thinking, you:
- Precisely identifying the anomalies
- You remove redundancies
- You remove irrelevant data
- You come up with filtered, credible data
And finally, you pick the essentials for solving the problem.
3. Creating/Synthesizing:
“Creativity is the Production of meaning by synthesis.” – Alex Faickney Osborne
You bring your original ideas, new framework, and fresh designs other than what you have analyzed and evaluated so far.
Words/verbs that correlates Higher Order Thinking Levels:
If you want to understand higher-order thinking, these words/verbs will be the one-word solution for you. You can correlate the words to understand the meaning of higher-order thinking.
Analyzing Level:
Action Verbs/Words are: Appraise, Assess, Check, Compare, Conclude, Criticize, Critique, Defend, Justify, and Support.
Evaluation Level:
Action Verbs/Words are: Choose, Combine, Compose, Construct, Formulate, Hypothesize, Organize, Plan, Produce and Role Play.
Synthesizing Level:
Action Verbs/Words are: Choose, Combine, Compose, Construct, Create, Design, Develop, Formulate, Hypothesize, Invent, Make, Makeup, Originate, Organize, Plan, Produce and Role Play
To summarize Higher Order Thinking:
“We are approaching a new age of synthesis. Knowledge cannot be merely a degree or a skill. It demands a broader vision, capabilities in critical thinking, and logical deduction without which we cannot have constructive progress.” – Li ka Shing

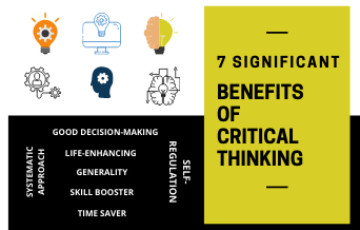
Find out the top 7 benefits of critical thinking in life. Enhance problem-solving, decision-making, and analytical skills for personal and professional success.
1. Critical Thinking is a life skill:
Critical thinking is a wonderful life skill. You can use critical thinking to make smart and strategic decisions. You can improve your studies, sharpen your skills, and boost your work performance through critical thinking.
Also, critical thinking enhances your creative thinking process. The best of all is that critical thinking compels you to look for credibility in everything.
2. Apply it anywhere:
Critical Thinking is a General Domain. You can apply it anywhere. If you are a student, critical thinking helps you to study well, do deep work, increase creativity, and gain more knowledge than what is in the book.
When it comes to the profession, critical thinkers are better problem-solvers and solution-givers than everyone seeks.
3. Enhances your performance:
Critical thinking skills enhance brain function with strategic, reasoning, and logical thinking. With these skills, you can improve your performance in any field.
4. Self-Reflection:
One of the key benefits of critical thinking is self-reflection. Critical thinkers will be good at self-regulation and self-reflection. It gives them confidence. They believe that everything starts with them.
5. Systematic approach:
A systematic approach is a significant attribute among all 7 benefits of critical thinking. You can succeed well when you handle everything systematically instead of reacting immediately.
6. Better Decisions:
Critical thinkers will not be easily deceived. They will not fall for false pretenses because they know when they see or hear them. There will be no emotional biases. It all leads to making better decisions.
7. Save Time:
You save time by removing the time-wasters from the equation, right? Critical thinking skills do exactly that. They help you identify skepticisms, ambiguities, and irrelevancies so you can easily remove them from the problem scenario. As a result, you save time, gain clarity, and gain more focus.
1. Good Analytics:
When you analyze a problem, you understand it better. Once you understand the problem, it becomes easy to formulate appropriate solutions.
Good analysis/analytical ability is always a top critical thinking skills that people look forward to.
2. Remembrance:
Your ability to remember and re-assemble information from your brain is a key skill in critical thinking. It helps you connect all scattered pieces of data in your brain to get the big picture.
3. Categorization:
To categorize problems based on any given criteria is a skill. It means you are trying to analyze and grasp the problem better.
4. Correlation:
Correlation is important to critical thinking for two reasons. First, correlation helps you find the connection between problem variables. Second is, you can find whether the data and arguments you collected apply to the problem. We need clarity to find suitable solutions.
5. Logical Reasoning:
Logical-reasoning makes us understand ‘what the fact is’ or ‘what the truth is’ behind everything. It commands your brain to see the truth beyond aesthetics. This ability to reason logically separates critical thinkers from the rest.
6. Evaluation:
Evaluation is an important critical thinking skill. By evaluating, you bring the needed credibility and trust to your findings and inferences.
7. Strategic Thinking:
Strategic thinking can bring new dimensions to the problems. Other then the usual process flow, strategic-thinking speeds up your problem-solving and critical thinking abilities.
8. Creative Thinking:
Creative thinking and critical thinking complement each other.
We consider creativity the most fun and interesting one among the top 8 critical thinking skills. This is where you bring fresh perspectives and innovative ideas to light.
The catchy phrases, stunning logos, sophisticated designs, and technologies we see today are all products of creative and critical thinking.

Let’s discuss the nine key characteristics of critical thinkers that make them stand out from the rest.
1. Separating Facts from Opinions:
A critical thinker will be good at differentiating facts and personal-opinions. They pick the right data. And, finally, they decide based on that right data. Critical thinkers will not decide only on emotions.
2. considering all options:
A fine quality seen among critical thinkers is that they listen to people. Critical thinkers welcome good ideas and fresh perspectives from other people rather than their sole action.
3. Facts before Feelings:
Critical thinkers decide realistically and logically. Critical thinkers go for what is right for the problem. They don’t decide based on what they feel is right.
4. The response over Reaction:
Critical thinkers are good responders. They know how to respond to a situation or a problem. Critical thinkers will be patient enough to analyze what is in front of them. Instantly reacting out is not what they do.
5. Validation before Reaction:
Critical thinkers do not believe everything they hear. They gather the details. They analyze the facts. And they respond.
Critical thinkers validate everything before reacting to it.
6. No Personal-Bias:
Critical thinkers will be good at withholding personal judgments. They will think “what is best” instead of personal inclinations.
7. Introspection:
Self-introspection helps critical thinkers in making logical and conscious-driven decisions in whatever they do.
8. Good Problem-solvers:
Critical thinkers are good problem solvers. It makes them good at all levels, starting from their education to the profession.
9. Empathy over Intelligence:
Critical thinkers show empathy. Humbleness is a part of them. They can bring people together easily. Though they approach things logically, they do care about emotions too.
Benjamin Bloom formulated a pyramid made of six key elements of critical thinking. The framework suggests that to excel in critical thinking, one has to go through the levels mentioned in the pyramid.
The six key elements of bloom’s critical thinking framework (revised) are:
- Knowledge/Remembering
- Understanding
- Applying
- Analyzing
- Evaluating
- Creating
Level 1: Knowledge/Remembering
An individual’s ability to:
· Grasp basic concepts
· Recall facts
· Define problems
· Remember from memory
· Ability to repeat or recollect information
Level 2: Understanding
An individual’s ability to identify, describe and define a problem. Also, this level is where an individual classifies and explains problem-associated factors. And recognize the key reasons behind problems.
Level 3: Applying
The ability to execute tasks or implement solutions the right way!
This level is where critical thinkers resolve, interpret, and schedule tasks and solutions.
Level 4: Analyze
This level is where an individual:
- Draws correlations
- Ask questions
- Does examinations
- Experiments multiple ideas
- makes comparisons
- Review previous groundworks
The actual Problem scenario gets shaped at this level.
Level 5: Evaluate
You have analyzed all the variables and have come to the last stand. On this fifth level, defend and justify your eventual decision/stand.
You should argue, defend, add value, add support, and explain why this last solution is right for the problem.
Level 6: Create
You resolve the problem by applying the final-solution. This level is where you implement your original ideas and works into assembly after justifying it.
How Bloom’s Taxonomy is related to Critical Thinking?
Bloom further divided the six key elements of critical thinking into two major categories called:
- Lower Order Thinking Skills: Knowledge, Remembering, Understanding, Applying
- Higher-Order Thinking Skills: Analyze, Evaluate, Create
Bloom suggests that to become a good critical thinker, one has to develop both Higher-Order and Lower Order thinking skills.